Conversational AI is becoming the "front desk" of modern banking. It answers questions, completes requests, and routes sensitive issues safely. It does this on chat and on calls, 24/7, with audit trails and guardrails.
This guide maps conversational AI to real banking workflows. You will get 12 high-impact use cases, sample flows, and the KPIs that matter.
Why conversational AI is growing fast in banking
Banks need to be faster, simpler, and available at all times. Customers want banking to feel like chatting, not filling out forms. Conversational AI works when it runs real workflows, not when it’s used as a gimmick.
Why now: better service, lower costs, 24/7
Customer service is the first driver. Banks want shorter queues and fewer repeats. Customers want help at midnight, not "please call during business hours".
Market pull is real:
- In banking specifically, conversational AI reached USD 2.13B in 2024 and is expected to grow at a 22.7% CAGR (2025-2033) to USD 16.14B by 2033.
In my experience building and reviewing voice workflows, the shift happens when teams stop treating AI as "FAQ automation". The real win comes when AI is wired into systems, with policy controls, and clean human handoff.
Retail banking is being reshaped by customers expecting immediate, personalized, 24-hour support (Deloitte, 2023). Banks are also using conversational AI to automate service delivery while keeping satisfaction high (KPMG, 2023).

Myths about conversational AI in banking (and what's true)
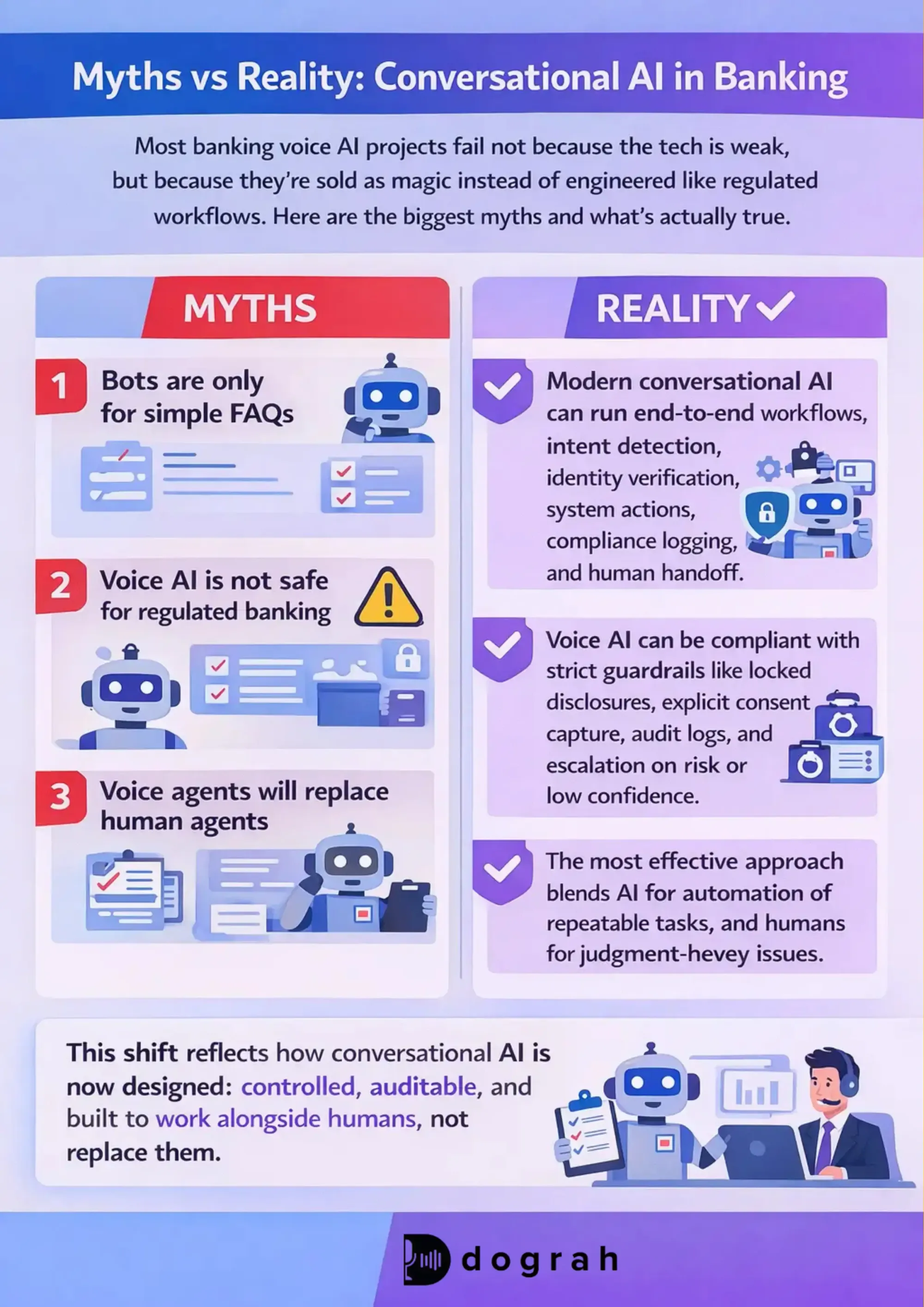
Most banking voice bot projects fail for simple reasons. They were sold as magic, not engineered like a regulated workflow. Let's clear the top myths early.
Myth 1: Bots are only for simple FAQs
Modern conversational AI can run end-to-end workflows like Dograh AI. The key is integration plus rules, not "better prompts".
What "real" looks like:
- Detect intent: "I want to block my card"
- Verify identity (OTP / KBA / step-up)
- Call tools/APIs (card system, core, fraud engine)
- Confirm action and send a written summary
- Log everything for compliance
- Handoff to a human with full context when needed
IBM describes this shift clearly: conversational AI is now used for customer support, self-service transactions, ID&V, onboarding, agent assist, multilingual support, reminders, and emotion-aware escalation.
Myth 2: Voice AI is not safe for regulated finance
Voice can be safe, but only with guardrails that are non-negotiable. You need controls that prevent off-script statements and unsafe actions.
Practical guardrails that work:
- Mandatory disclosures with script locking
- Consent capture with storage and timestamps
- Confidence thresholds and safe fallbacks
- Audit logs, call recordings, and traceable tool calls
- Escalation on distress, refusal, or low confidence
I have seen voice agents perform well in regulated settings when disclosures are treated like code. No free-form during regulated segments. No exceptions.
Myth 3: Voice agents will replace all human agents
The most effective approach blends AI for automation of repeatable tasks, and humans for judgement-heavy issues.
A good banking roadmap often looks like:
- Phase 1: Self-service intents + safe handoff
- Phase 2: Agent assist (real-time suggestions + summaries)
- Phase 3: Outbound automation (reminders, activation, status nudges)
- Phase 4: More action bots with strict policy controls
Glossary (key terms)
- Script locking: A control that forces the agent to use regulator-approved wording for disclosures and sensitive statements. It prevents the AI from improvising during compliance-critical parts of a call.
- Policy-based offer control (via rules engine): A pattern where eligibility, pricing, and offers are not generated by the model. They are pulled from an approved rules engine, so the AI can only present valid options.
- Right-party contact rate (RPC): In outbound calling, the percentage of calls where you successfully reach and confirm you are speaking to the intended person (not a wrong number or unrelated household member).
- KBA (Knowledge-Based Authentication): Identity verification using personal questions (like previous address or account details). It can be useful but has risk when data is widely exposed, so it is often paired with OTP or step-up methods.
- Step-up authentication: Triggering a stronger identity check (like OTP or biometrics) when the user attempts a higher-risk action (like blocking a card or disputing a transaction).
What conversational AI in banking is and how it works ?
Conversational AI in banking is not "a chatbot". It is a channel layer for banking workflows, backed by systems and controls. Think of it as a digital banker that can speak and type.
Simple definition: conversational AI in banking (chat + voice)
Conversational AI in banking uses AI to talk with customers in natural language. It works in chat and voice, and it can both answer questions and complete actions.
Common channels:
- In-app or web chat (inside digital banking)
- WhatsApp and SMS support
- Voice assistants for inbound support
- IVR replacement or "IVR with intent"
- Outbound calling for reminders and activation
How a banking voice agent works step-by-step
A safe banking call flow is structured, not improvisational. Here is the pattern I recommend for most voice agents:
- Greeting + disclosure "This is a digital assistant calling on behalf of Bank X..."
- Purpose + consent checkpoint Recording consent, communication consent, and offer consent (if relevant)
- Identity check Light verification first, then step-up if action is sensitive
- Intent detection "Are you calling about a card, a loan, or an account issue?"
- Tool/API calls Core banking, card system, CRM, LMS, ticketing, KYC provider
- Response in plain language No jargon. Confirm key values.
- Confirmation step "Do you want me to proceed?" before irreversible actions
- Summary message Send via SMS/WhatsApp/email with the next steps
- Logging + audit Transcript, tool calls, consent timestamps, disposition
- Handoff (if needed) Transfer to agent with context, not "start over"
What systems it connects to (the real work)
The value comes from integration. Without it, you only get a talking FAQ.
Typical integrations in banks:
- CRM (lead creation, disposition, customer profile)
- Core banking (balances, transactions, account status)
- Card management system (block/unblock, activation, limits)
- Loan Management System (LMS) (EMI status, delinquency bucket, promises)
- KYC provider (status checks, document workflow, video KYC links)
- Knowledge base (approved policies, fees, product FAQs)
- Consent + call recording system (storage, retrieval, audit)
- Rules engine (eligibility, offers, hardship options)
- Analytics (containment, AHT, conversion, opt-out)
- Omnichannel (WhatsApp/SMS/email for summaries and links)
If you’re implementing conversational AI with a contact-center stack, Dograh AI help to route calls, detect intent and run safe, policy-driven workflows. Even if you don’t use a traditional CCaaS stack, the pattern still holds: intent routing, scripted disclosures, consent capture, system integrations, and controlled human handoff.

Top benefits of conversational AI for banks and customers (with metrics)
Conversational AI works when it improves outcomes, and when it "sounds human". Banks should measure fewer repeats, faster resolution, and better conversion. Customers should get help faster and understand things more clearly.
Customer benefits: faster help, 24/7, simple language education
Customers notice speed and clarity first. They remember when they did not need to visit a branch.
Common customer-facing benefits:
- 24/7 answers and service requests
- Faster resolution for routine needs (balance, statements, card status)
- Clear explanations of products (rewards, EMI, fees) in simple language
- Multilingual support (especially useful in diverse markets)
- Better onboarding guidance (what to do next, what is missing)
- Less time on hold, less repeating information
A quote that matches what customers actually want: "Chatbots are available 24/7 for fast and immediate answers... helping reduce wait times, improve availability and be autonomous" (Capgemini, 2023).
Bank benefits: lower call costs + better conversion
Banks care about cost, efficiency, and controlled growth. Conversational AI can deliver all three when tied to KPIs.
Track KPIs that tie directly to business results, such as how many requests are resolved without an agent, reductions in handling time and cost per contact, first-contact resolution, conversion and activation rates, speed of follow-up, and how effectively missed calls are recovered.
Where voice helps most vs chat (calls, reminders, urgent issues)
Chat is great when users are already in-app. Voice is better when urgency, attention, or accessibility matters.
Voice tends to win for:
- Payment reminders and collections support
- Fraud alerts and immediate card blocking
- Card activation and education calls
- Appointment booking and callbacks
- Less tech-savvy segments who prefer speaking
- "You must act now" flows, where reading is too slow
Banks use Dograh AI for both inbound and outbound in banking, handling inbound calls with intent routing, authentication, and safe handoff, while outbound voice closes loops through consent-led reminders, activations, and follow-ups with strict frequency and compliance controls.
12 High-impact conversational AI use cases across banking workflows (with sample flows + KPIs)
These are the use cases, repeated across banks. Most are not "chat or voice only". They are workflow automation with a conversation layer. For each use case, I include: what it does, integrations, guardrails, and KPIs.
1) Retail customer support: balance, transactions, statements, service requests
This is the highest-volume starting point for most teams. It is also the fastest place to prove containment and AHT impact.
Sample flow (voice or chat):
- Disclosure + consent (if voice)
- Verify identity (light or step-up depending on data access)
- Intent: balance / last transactions / statement request / address update
- Tool calls:
1. Core banking (balance, transactions)
2. Statement system (generate statement link)
3. CRM (case logging)
- Confirm the result and send summary via SMS/WhatsApp/email
- Handoff if user disputes data or asks for exceptions
Integrations needed:
- Core banking
- Knowledge base for policy answers
- CRM/ticketing
Compliance notes:
- Use tool-only facts for balances and transactions
- Mask account numbers in spoken responses
- Log every data access request
KPIs:
- Containment rate by intent
- AHT and transfer rate
- CSAT / post-interaction rating
- Repeat contact rate within 7 days
Real-world examples exist at scale. For instance, Bank of America's Erica has handled over 1 billion interactions, spanning tasks like balances and guidance.
2) Fraud and risk: fraud alerts, card blocking, dispute intake
Fraud flows must be short, strict, and heavily verified. This is where voice can be a serious advantage due to speed.
Data Security & Residency (Dograh): Fewer data hops make privacy and security easier to manage, while open-source availability helps meet data residency requirements with greater control.
Sample flow:
- Disclosure: "fraud safety call"
- Step-up identity check (OTP recommended)
- Confirm suspicious transaction(s)
- If fraudulent:
1. Block card (tool call)
2. Create dispute ticket
3. Issue replacement workflow (if supported)
- Send confirmation message
- Handoff to fraud agent if user is unsure or high-risk
Safety controls:
- Step-up auth required for blocking/disputes
- Audit logs for tool calls
- Abuse detection (scammers may try to social-engineer the agent)
- Optional voice biometrics as an added signal (not the only factor)
KPIs:
- Time-to-block (minutes)
- Fraud case intake completion rate
- Fraud loss avoided (estimated)
- False escalation rate
IBM notes fraud detection is a major value area: 61% of bank executives say fraud risk detection will provide the biggest boost to business value (cybersecurity close behind at 52%).
3) Onboarding + KYC guidance calls (status checks + completion nudges)
KYC is where drop-offs happen. A voice agent can reduce confusion and push completion without adding headcount.
Detailed voice flow (recommended):
- Greeting + disclosure: digital assistant
- Consent: recording + data access consent
- Fetch customer KYC status via webhook (Dograh AI) to call your own API's or any other workflows (do not read raw PII out loud)
- Explain status in plain language:
1. "Your PAN is verified, but address proof is missing"
- Offer next step:
1. send a secure upload link via SMS/WhatsApp/email
2. or connect to human / video KYC
- If customer agrees to video KYC now:
1. handoff rules trigger agent or schedule callback
- Log outcomes:
1. completed / link sent / refused / unreachable
Integrations needed:
- CRM for customer and lead state
- KYC provider for status and next-step links
- Messaging channel (WhatsApp/SMS/email)
- Consent store + call recording
Guardrails:
- Mask PII
- Do not accept documents over insecure channels
- Do not continue without clear consent checkpoints
KPIs:
- KYC completion rate
- Drop-off rate by step
- Time-to-KYC completion
- Callback scheduling success rate
This matches what I see in practice: KYC voice use cases work when they are wired into CRM and KYC systems with guardrails and a clean handoff.
4) Lending: pre-qualification, document reminders, application status
Lending flows are a strong fit for conversational AI because the path is structured. Keep eligibility decisions policy-driven.
Sample flow:
- Disclosure + consent
- Quick pre-qualification questions (income band, employment type, city)
- Rules engine call for eligibility range (not model-generated)
- Create/update lead in CRM and LMS
- Document reminders:
1. list missing docs
2. send upload link
- Schedule branch/video call if needed
- Status checks:
1. "Your application is under review, next update in 24-48 hours"
Integrations needed:
- CRM + LMS
- Rules engine for eligibility and product matching
- Website widget deployment
- Messaging for reminders and links
KPIs:
- Speed-to-lead (first contact time)
- Application completion rate
- Approval cycle time
- Drop-off reasons captured
5) Retail banking product education (fees, rewards, EMI, interest basics)
This is underrated and high leverage. Better understanding reduces complaints and increases product usage.
What the agent does:
- Explains product terms in plain language
- Checks understanding ("Would you like me to repeat that?")
- Sends a written summary so the user does not forget
Integrations:
- Approved knowledge base (policy-locked)
- Multilingual voice support up to 30 languages
- CRM notes for what was explained
KPIs:
- Reduction in "what is this fee" tickets
- Complaints rate
- Product activation and usage uplift
6) Missed-call recovery and callback automation
Missed calls hurt satisfaction and sales. A voice agent can call back quickly and route correctly.
Flow:
- Call back within X minutes
- Ask intent and verify identity if needed
- Resolve or schedule a human callback
- Log disposition in CRM
KPIs:
- Callback completion rate
- Abandonment rate
- Time-to-first-response
7) Payment issues and charge explanations (bill pay failures, card declines)
These calls are emotional. The agent must stay calm and factual. For fast diagnosis and a clean escalation path.
Flow:
- Identify issue type (decline, failed transfer, bill pay failure)
- Tool call to fetch reason codes
- Provide next step: retry, update limits, talk to fraud team
- Escalate if the reason is unclear or high risk
KPIs:
- First-contact resolution rate
- Transfer rate by reason code
- Time-to-resolution
8) Dispute intake (chargeback initiation and tracking)
Disputes are process-heavy but predictable. A conversational flow can gather structured data cleanly.
Flow:
- Step-up auth
- Capture dispute details (merchant, date, amount, reason)
- Create ticket, provide tracking ID
- Send summary by message
- Status check later via chat or voice
KPIs:
- Dispute intake completion rate
- Time-to-create ticket
- Rework rate due to missing information
9) ATM / branch issue reporting (cash not received, card retained)
These issues need fast acknowledgement and tracking. Users mainly want a reference number and next steps.
Flow:
- Verify identity if account-level details are discussed
- Collect incident details
- Create ticket and provide SLA disclaimer
- Route to operations team
KPIs:
- Time to provide reference ID
- Ticket quality score
- Repeat contacts on same issue
10) Agent assist inside the contact center (real-time help)
This is often the fastest way to show ROI without full automation. It reduces AHT and improves consistency.
Agent assist can:
- Transcribe calls
- Suggest next best actions
- Surface policy snippets
- Prompt mandatory disclosures
- Auto-summarize and auto-disposition
KPIs:
- AHT reduction
- QA compliance score
- After-call work time reduction
11) Multichannel support: WhatsApp/SMS + web/app chat continuity
Customers hop channels. Banks should not lose context. This is where omnichannel handoff matters.
Flow idea:
- Start in voice, send link in WhatsApp
- Continue in chat for document upload
- Return to voice for final confirmation
KPIs:
- Cross-channel completion rate
- Drop-off rate at channel switch
- Time-to-complete journey
12) Proactive service notifications (maintenance, outages, policy updates)
This is not sales. This is trust. A voice agent can reduce inbound spikes during disruptions.
Flow:
- Notify impacted customers
- Offer status and expected resolution time
- Provide self-serve options and escalation path
KPIs:
- Reduction in inbound volume during incident
- Complaint rate during incidents
- Message delivery and acknowledgement rates

More banking voice AI use cases (outbound + operations)
Outbound and operations are where voice works best and where compliance issues surface fast if handled carelessly. Treat outbound as a regulated product, not a growth hack.
Collections and payment reminders (EMI due, delinquency support)
Collections must be respectful, controlled, and measured. A good agent supports the customer while protecting the bank.
Compliant flow:
- Disclosure + reason for call
- Right-party confirmation (RPC)
- Share due amount and date (only after correct verification level)
- Offer options:
1. payment link
2. short extension if policy allows
3. connect to trained agent
- Detect distress or refusal and escalate or end politely
- Log promise-to-pay and schedule follow-ups within frequency limits
Integrations:
- LMS (due amounts, delinquency bucket)
- CRM notes
- Payment link generator
- Consent/opt-out store
KPIs:
- RPC (Right-party contact rate)
- Promise-to-pay rate
- Roll rate (movement into worse delinquency buckets)
- Opt-out rate
- Complaint rate
A practical industry note: UniCredit has discussed using AI to improve debt collection via segmentation and personalized reminders. Use this as inspiration for segmentation and tone, not as a blueprint for your compliance rules.
Card activation + education + upsell (detailed example)
This is one of the cleanest voice ROI workflows when done safely. It combines activation, education, and relevant offers, with strict controls.
Outbound call flow (production-style):
- Outbound call to newly approved customer
- Identity verification (DOB and/or OTP)
- Mandatory recorded disclosures + consent checkpoints
- Explain benefits in simple language:
1. rewards
2. EMI on spends
3. lounge access (if eligible)
- Confirm intent to activate
- Activate:
1. guide the user through app steps, or
2. do backend activation via card system tool call (if allowed)
- Detect spend intent (travel, gadgets, fuel) with simple questions
- Offer relevant add-ons:
1. EMI plan options
2. add-on card
3. insurance Only from the rules engine and eligibility system.
- Confirm acceptance clearly (no ambiguous consent)
- Send summary on WhatsApp/SMS
- Log consent + call details + offer presented and accepted
Guardrails (non-negotiable):
- Scripted disclosures with script locking
- Consent checkpoints (recording, data use, offer consent)
- No deviation from approved offers
- Confidence thresholds for intent detection
- Fallback to human agent on confusion or refusal
Integrations:
- CRM (campaign, customer record, disposition)
- Card management system (activation, status)
- Consent + call recording system
- Rules engine (eligibility and allowed offers)
- WhatsApp/SMS for summary
- Analytics dashboard for performance
KPIs:
- Activation rate
- Upsell acceptance rate (only for eligible, consented offers)
- Complaint rate
- Drop-off rate at OTP step
- Transfer-to-agent rate
If you want a second example from India, HDFC Bank's EVA is positioned to handle a wide range of queries and supports 24/7 service. The important part is intent coverage and how it reduces agent load.
Branch/service appointment booking and callbacks
Appointment booking reduces branch chaos and improves experience. Voice is strong here because it feels like talking to reception.
Appointment booking flow:
- Identify intent: "book appointment" / "callback"
- Collect basics: service type, preferred branch/city
- Query available slots (tool call)
- Confirm slot and details
- Send calendar link and confirmation via SMS/WhatsApp
- Create CRM task
- Reminder message before the appointment
KPIs:
- Show-up rate
- Reduced wait time
- Reduced inbound calls to branch
- Reschedule rate
Security, privacy, and compliance guardrails (banking checklist)
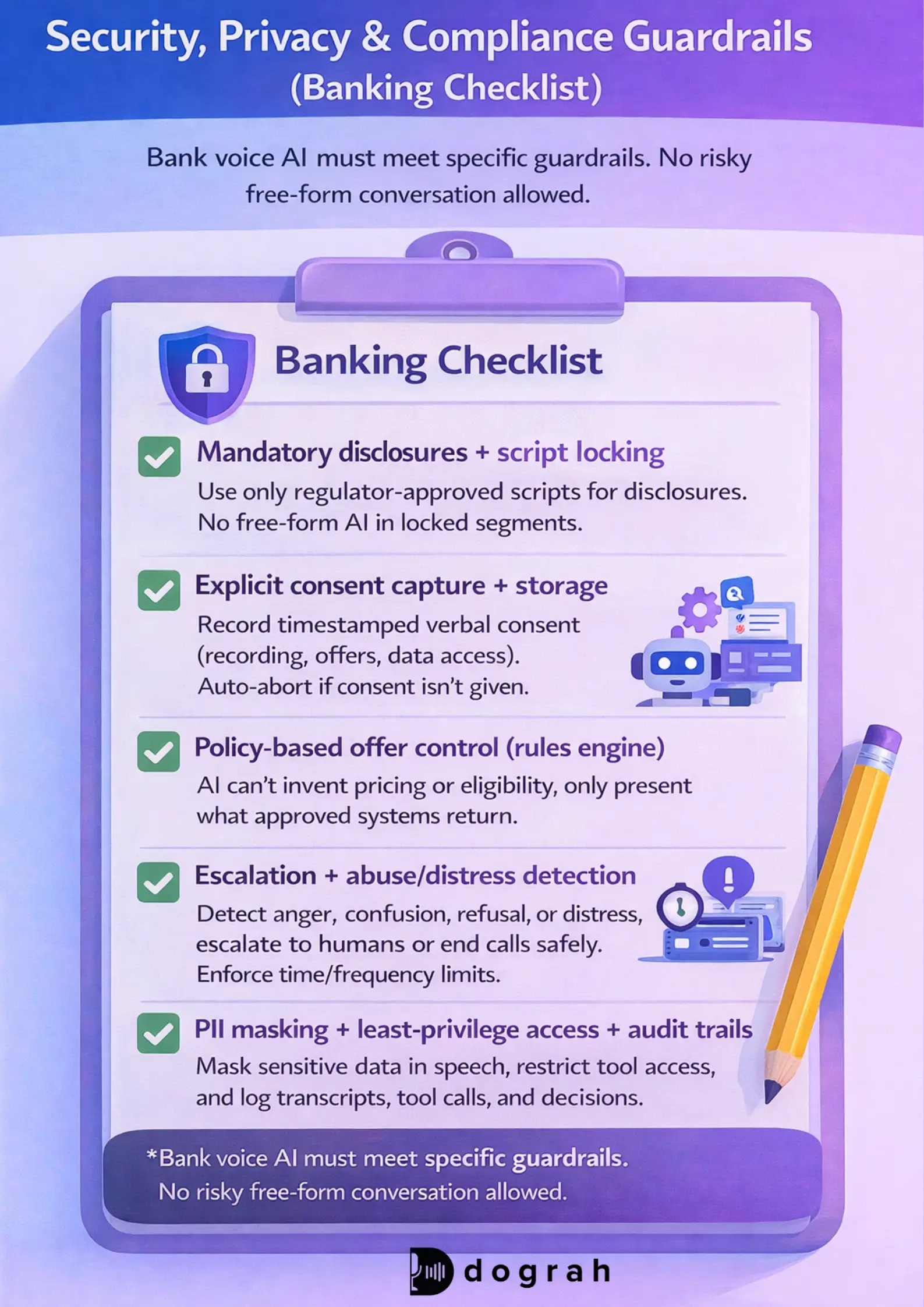
Compliance is not a feature. It is the product. If you cannot prove what was said and why, you will not scale. Build controls first, then scale coverage.
Top 5 guardrails to require before launch
These five controls cover most early failures. They are also the easiest to audit.
- Mandatory disclosures + script locking Regulator-approved scripts only for disclosures and sensitive statements. No free-form generation during locked segments.
- Explicit consent capture + storage Timestamped verbal consent stored with call ID. Separate consent for recording, offers, and data access. Auto-abort if not granted.
- Policy-based offer control via rules engine The AI cannot invent pricing, eligibility, fees, or relief options. It can only present what the policy tool returns.
- Escalation + abuse/distress detection with strict limits Detect anger, confusion, refusal, distress. Escalate to trained humans or end call politely. Enforce call-time and frequency limits.
- PII masking + least-privilege access + audit trails Mask sensitive values in speech. Keep tool access minimal. Log tool calls, transcripts, and decisions.
Identity checks: OTP, KBA, and voice biometrics (when to use)
Identity is not one-size-fits-all. Match verification strength to action risk.
OTP
- Strong for high-risk actions (block card, dispute initiation)
- Works well in omnichannel flows (voice call + OTP via SMS)
KBA
- Useful for lower-risk confirmation when OTP is not possible
- Risk: answers can be leaked or guessed, so avoid using KBA alone for sensitive actions
Voice biometrics
- Helpful as an additional signal, especially for repeat callers
- Should not be the only factor for regulated actions, depending on your risk posture
Rule of thumb I use:
- Read-only info (general product info): no auth
- Account-specific info (balance/transactions): light auth
- Irreversible actions (block, dispute, limit change): step-up auth (OTP)
What is step-up authentication in banking voice flows?
Step-up authentication means increasing verification strength when risk increases. It is how you safely let customers do more than ask questions on voice.
In a voice flow, step-up usually triggers when:
- The customer requests a sensitive action (block card, dispute, address change)
- The system detects unusual patterns (new device/number, high-risk geography)
- The customer fails basic verification or the model confidence is low
Implementation pattern that works:
- Start with light checks (name + partial info, or "confirm last 2 digits" where allowed)
- Trigger OTP for actions that change state
- Log the step-up event and its result (success/fail/timeout)
- If step-up fails, do not continue. Route to a human or ask to visit a secure channel
Tool-only actions matter here. The AI should not decide risk policy. The policy engine should.
Integration guide: connecting conversational AI to bank systems
Integrations decide whether your agent is helpful or causes problems. In practice, most time goes into orchestration and data plumbing. A common rule in real projects: prompts are 10%, orchestration is 90%.
Reference architecture (voice stack + tools)
A bank-grade conversational stack typically includes:
- Telephony layer (inbound/outbound routing)
- STT (speech-to-text)
- LLM (dialogue control, constrained by policies)
- TTS (text-to-speech)
- Workflow/orchestration layer (state, retries, validation)
- Tool calling to bank systems (core, CRM, LMS, card)
- Knowledge base / RAG for approved content
- Analytics and QA (intent success, escalations, compliance checks)
- Call recording + consent store
- Rules engine for eligibility and offer controls
A practical architecture warning from builders: do not connect an LLM directly to core banking. Use an orchestrator that validates entitlements, schemas, and limits first. A community discussion captures this well: "the bottleneck is orchestration, not the model." Reddit discussion on orchestration as the bottleneck.
Common webhook patterns (status checks, updates, and follow-ups)
Webhooks are how conversational AI becomes operational. Here are patterns that show up in banking projects repeatedly:
- Fetch KYC status GET /kyc/status?customer_id=...
- Update CRM disposition POST /crm/disposition {call_id, outcome, next_action}
- Create ticket (fraud/dispute/branch issue) POST /tickets {type, customer_id, summary, priority}
- Trigger WhatsApp/SMS summary POST /messages/send {channel, template_id, variables}
- Schedule callback POST /callbacks {customer_id, slot, reason}
- Update LMS promise-to-pay POST /lms/ptp {loan_id, date, amount}
If you implement these with strict schemas and retries, your agent becomes reliable. If you skip this, you get hallucinations and broken promises.
Omnichannel handoff: voice to SMS/WhatsApp/email and to human agent
Handoff is not "transfer the call". It is transferring context, safely.
Rules that usually trigger handoff:
- Low confidence or repeated misunderstanding
- Customer explicitly asks for a human
- High-risk or regulated actions that require human review
- Escalation signals: distress, anger, confusion
- Tool/API failures
What context should transfer:
- Intent and slots (what user wants)
- Verification status (what checks passed)
- Last tool/API results
- Transcript and a short summary
- Customer preference (language, channel, time)
Challenges and best practices (what breaks in real banking rollouts)
Most failures look the same. Bad promises, unclear disclaimers, and messy integrations. You can avoid these with a few strict practices.
Avoiding bad experiences: no hallucinated offers, clear disclaimers
Banks must avoid creative outputs. This is regulated communication.
Best practices that work:
- Use approved scripts for disclosures and product claims
- Use tool-only facts for rates, fees, eligibility, balances
- Add confirmation steps before any state-changing action
- Use policy tools for offers and hardship options
- Do not guess when systems are down, acknowledge and escalate
- Provide a written summary for anything important
Language, accents, and multilingual support
Multilingual voice is not optional in many regions. Accent and code-switching (mixed languages) can break STT quickly.
Practical approach:
- Start with top languages by volume
- Measure STT accuracy and intent success by locale
- Add "repeat in another language" options early
- Use human review on low-confidence locale segments
- Keep language simple and consistent in scripts
Future trends: where conversational banking is going next
The next wave is not "better chatbots". It is action voice bots that complete tasks safely.
LLMs + tool use: from chatbots to action voice bots
The shift is from just answering questions to actually taking action. In banking, taking action requires clear policy controls and full auditability.
What is changing:
- LLMs become a reasoning layer
- Tools become the source of truth
- Orchestration becomes the safety layer
- Rules engines control offers and eligibility
Voice-first banking inside contact centers
Voice is becoming a front door, not only a support channel. Voice agent is becoming the fastest safe automation path.
Voice Agent assist trends:
- Voice agents handle routine banking requests 24/7 without queues.
- Voice runs real banking tasks, not just FAQs or forms.
- Calls are resolved on the first contact with less handoff.
- Guardrails, logging, and handoffs are built in from day one.
- Agents connect directly to core banking systems and APIs.
Hyper-personalization with strict consent and auditability
Personalization will grow, but consent will decide what is allowed. Banks should practice minimization: only use what is needed for the journey.
A practical personalization model:
- Use CRM history to tailor reminders and education
- Respect channel preferences and opt-outs
- Keep offers policy-driven via rules engines
- Log why a suggestion was made (audit trail)
A public example of personalization impact: JPMorgan Chase has stated that AI-driven personalization helped increase revenue by more than $500 million (shared at its 2023 Investor Day materials and communications). Use this as directional evidence that personalization can be material, but measure your own lift carefully.
How Dograh fits: open source voice AI agents for banks (practical)
Banks and fintech teams should prefer control over lock-in. You need workflows that are easy to audit and change. Open source and self-hosting can be the right choice when governance and data control are non-negotiable.
Why open source voice AI matters in finance (control + self-hosting)
Open source helps in regulated environments because it improves visibility. You can inspect workflow logic, data paths, and logging behaviors.
Dograh is an open source voice AI platform for building calling agents:
- Drag-and-drop workflow builder
- Build and edit flows in plain English
- Bring-your-own telephony, STT, LLM, and TTS
- Webhooks to call your APIs and banking systems
- Cloud-hosted or self-hosted deployment
- Multilingual and multiple voices
- Extract variables from calls and trigger follow-up actions
- Custom STT Dictionary: Add business-specific terms so the system understands nuanced language correctly (e.g., “kay why see” → KYC, HbA1c, “BP high,” OPD)
- Multilingual voice support up-to 30 languages
This matters in finance because:
- You can control where data flows
- You can enforce script locking and policy tool calls
- You can keep audit logs consistent with your compliance needs
- You reduce dependency on closed vendor behavior
Dograh is positioned as an open source alternative to platform-style voice stacks, with a commitment to remaining FOSS.
Build a sample banking voice workflow in minutes (drag-and-drop)
Fast iteration is useful, but only if you still ship safely. Here is a workflow you can build quickly in Dograh.
Example: KYC guidance voice agent
- Define intents:
"check my KYC status"
"complete KYC now"
"send link"
- Add a Disclosure node (locked script)
- Add Consent capture nodes:
recording consent
data access consent
- Add Webhook node:
fetch KYC status from your KYC provider
- Add Decision node:
if status = pending documents -> send upload link
if status = needs video KYC -> offer handoff or schedule
- Add Omnichannel node:
send WhatsApp/SMS/email summary + secure link
- Add Fallback + human handoff:
low confidence
repeated confusion
customer request
- Log variables:
outcome, next action, consent timestamps, and tool call IDs
Plain-English workflow editing helps because banking flows change often. If every change requires a code release, you will ship slower than policy changes.
Testing with Looptalk (AI-to-AI) for compliance and edge cases
Testing voice agents with humans alone is slow and inconsistent. You need repeatable stress tests.
Dograh includes an AI-to-AI testing suite called Looptalk (work in progress). AI-to-AI testing means using one AI agent to test another AI agent. In voice, it helps you generate thousands of consistent test calls quickly. The idea is simple: simulate customer personas that call your agent and try edge cases.
Closing note
Conversational AI in banking is growing because it meets two needs at once: better customer experience and lower operational load, with measurable KPIs.
If you are building voice workflows, start with one high-volume intent. Wire it to tools, lock scripts, capture consent, and track metrics weekly. Then expand to fraud, KYC, lending, and outbound workflows.
My bias: banks should stop buying "general-purpose" assistants for regulated work. Buy (or build) narrow, instrumented workflows that can be audited end-to-end. That is what scales.
Related Blog
- Discover the Self-Hosted Voice Agents vs Vapi : Real Cost Analysis
- A Practical Cost Comparison Self-Hosted Voice Agents vs Bland: Real Cost Analysis (100k+ Minute TCO)
- A Practical Cost Comparison Self-Hosted Voice Agents vs Retell: Real Cost Analysis (TCO Tables + $/Min).
- Explore Conversational AI for Sales: Essential Guide [Dograh vs LiveKit/Pipecat]
- See how 24/7 Virtual Receptionist Helps Small Firms Win More Clients by boosting responsiveness and improving customer engagement.
- Explore Conversational AI in Insurance: Ultimate Guide (Voice Agents + FNOL)
- Check out Contact Center Automation Trends: Ultimate Guide (2026 Roadmap + Open-Source Voice Agents)
FAQ's
1. What is conversational AI in banking ?
Conversational AI in banking uses a Dograh-powered AI voice agent to let customers handle routine banking tasks by speaking naturally, while securely escalating sensitive issues to human agents with full compliance.
2. How does conversational AI improve customer service in banking ?
Conversational AI in banking speeds up service by using a voice AI agent to answer FAQs instantly, authenticate users, and resolve or route issues with full context, no waiting or repetition.
3. How can AI be used in banking?
AI can be used in banking through conversational AI on voice, where a voice agent handles FAQs and customer queries. With guardrails, it extends to onboarding, KYC guidance, card activation, fraud checks, and sales automating routine work while improving speed and control.
4. How do banks keep conversational AI compliant and secure ?
Banks keep conversational AI compliant and secure by enforcing strict guardrails like locked disclosures, explicit consent capture, policy-based actions, and audited system integrations. Any risk or uncertainty triggers immediate escalation to a human agent.
5. Can an open-source voice AI platform work for banking call automation?
Yes. An open-source voice AI platform can work for banking call automation platforms like Dograh AI can be self-hosted, reducing third-party hops while making privacy, security, and data-residency compliance easier due to their OSS nature.
Was this article helpful?

